Advertisement advertisements
Hearing Difficulty in Children: Symptoms, Care and Diagnosis. Hearing plays a crucial role in the development of childhood learning.
Unfortunately, some children face hearing difficulties, which can negatively affect their quality of life and academic performance.
In this article, we will discuss the symptoms of hearing difficulty in children, the necessary care and how to make an adequate diagnosis.
See also:
Advertisement advertisements
A Luz Baby is one of the best stores of infant products. Click here.
Symptoms of Hearing Difficulty in Children
Identifying hearing difficulties in children can be a challenge, because symptoms can vary depending on the severity of the problem. Here are some common sinais to be observed:
Late speech: Children with hearing difficulties often experience significant delays in the acquisition of language and non-development of language.
Difficulty in following instructions: If a child does not respond adequately to simple verbal commands or has difficulty understanding and following instructions, this may indicate a hearing problem.
Television or radio volume excessively loud: If a child always prefers to increase the volume of the television or radio at an uncomfortably high level, it could be a sign that it is difficult to hear.
Concentration problems: Children with hearing difficulties may have difficulty concentrating in the classroom or in noisy environments, due to sensory overload.
Delays in failure and non-development of language: In addition to late speech, children may experience difficulties in articulating words correctly or in understanding and using languages correctly.
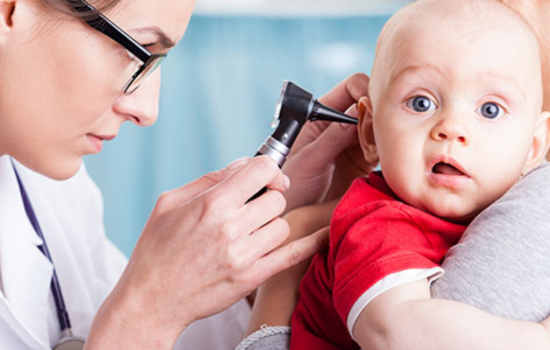
Care for Children with Hearing Difficulties
If you suspect that your child is facing hearing difficulties, it is important to seek appropriate care or as much as possible. In summary, here are some important measures to be taken:
Consult a specialist: Schedule a consultation with an otorhinolaryngologist or a speech therapist specialized in children's hearing. They can carry out tests and exams to validate the hearing of children and determine the degree of difficulty.
Favorable environment: Create a favorable environment at home and in school for children with hearing difficulties. Reduce background noise, face forward to speak and use body language to assist in communication.
Educational support: Children with hearing difficulties can benefit from specialized educational interventions, such as support classrooms or speech therapy. Therefore, these interventions can help develop communication skills and minimize the impact of unlearned hearing difficulties.
Emotional support: Lidar with hearing difficulties can be challenging for both children and families. In short, it is essential to provide adequate emotional support. Finally, make sure that children feel understood, encouraged and valued.
Also, communicating openly about hearing difficulties and seeking support resources, such as support groups or family therapy, can be very helpful.
Assistive technologies: In many cases, the use of assistive technologies, such as hearing aids or cochlear implants, can significantly improve children's hearing. Then, consult a specialized professional to determine which option is most appropriate for your child's case.
Diagnosis of Hearing Difficulty in Children

For an accurate diagnosis of hearing difficulties in children, different tests and exams must be carried out. Here are some of the most common diagnostic techniques:
Hearing triage testsThese rapid, non-invasive tests are only used to identify possible hearing problems in newborns and small children. They generally involve the presentation of sounds and the observation of auditory responses.
Audiometry: Audiometry is a test that measures hearing and the ability to distinguish between different sounds. It is performed by an audiologist and can be adapted to the child's personality and abilities.
Auditory Evoked Potentials: These tests record the electrical activity of the brain in response to sound stimuli. They help to evaluate the integrity of the auditory system and identify possible dysfunctions.
Language and development support: In addition to two auditory tests, it is important to carry out a comprehensive assessment of language development and child communication skills. This may involve standardized assessments, clinical observations and questionnaires for the country.
Conclusion
The difficulty of hearing in children can have a significant impact on their overall development and academic performance. It is essential to be attentive to signs of hearing difficulty and seek appropriate care or as much as possible.
In short, consulting specialized professionals, creating a favorable environment, providing educational and emotional support, in addition to using assistive technologies, are important measures to help children overcome the challenges associated with hearing difficulties.
Pois, an accurate diagnosis and an early intervention can make a difference in linguistic development and not to be general in children, allowing them to reach their full potential.

Notes: The materials and information on the Universo Família page are not intended for medical diagnosis, nor should they be used as such. You should always consult a doctor or qualified health professional about your real needs..
Sources for research
When creating a text with information about the difficulty of listening to children, it is important to base it on reliable and up-to-date sources. Here are some suggested sources that you can use to research the topic further:
American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA) – ASHA is a professional organization that provides resources and information about speech, language, and hearing. The site (https://www.asha.org/) contains articles, guides and research related to hearing difficulties in children.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) – The CDC is a United States health agency that provides open information on a wide range of health conditions. The CDC site (https://www.cdc.gov/) can be a reliable source for obtaining statistical data, hearing triage guidelines and information on the impacts of hearing difficulties in children.
American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) – The AAP is an organization dedicated to children's health and provides clinical guidance to doctors and families. The AAP site (https://www.aap.org/) contains information on the assessment, diagnosis and treatment of hearing difficulties in children.
National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD) – The NIDCD is a research institute of the United States government that focuses on questions related to hearing, communication, and language disorders. In addition, the NIDCD site (https://www.nidcd.nih.gov/) offers resources and updated information on hearing difficulties in children.
World Health Organization (WHO) – The WHO is a specialized agency of the United Nations that works to promote global health. The WHO site (https://www.who.int/) can provide information on the prevalence, impact and intervention strategies related to hearing difficulties in children on a global level.
Therefore, it is always necessary to verify the credibility of sources, looking for information from organizations and institutions established in the area of health and hearing research.